
Energy Development
Manitoba Deserves Transparency on Energy East
Source: Winnipeg Sun
In the 30,000-page project application filed with the National Energy Board (NEB), the project plans state that Manitoba is expected to own the infrastructure needed to power the nine new pump stations proposed within the province. Manitobans – through Manitoba Hydro – would need to invest in transmission lines for use of public hydropower to move the dirtiest oil on the planet. “People in this province need to hear about the tremendous investment this proposed pipeline needs from us in Manitoba,” said Eric Reder, Manitoba Campaign Director for the Wilderness Committee. “The large pumping stations needed to push bitumen across Manitoba will require 176 megawatts of power. This is roughly as much as the Wuskwatim dam generates.” Alex Paterson of the Manitoba Energy Justice Coalition said what’s missing in the debate over Energy East is how Manitoba Hydro fits into the building of a national oil pipeline. "We have a right to clear and informed information about the implications of our energy decisions in the province," Paterson said. "It also means that Manitobans of any stripe collectively deserve a right to say ‘no’ to any energy project." Gaile Whelan-Enns, Manitoba WIldlands Director, said, “It’s time for Manitoba’s government to admit how many leases, work permits, water permits, and environmental licences they would issue to Energy East.’
View May 8, 2015 DeSmog Canada article Oil Development Another spill has occurred on a pipeline operated by Canadian Company Enbridge Inc. Another spill has occurred on a pipeline operated by Canadian Company Enbridge Inc.Approximately 200,000 litres (1,200 barrels) of bitumen spilled from a pipeline in rural Wisconsin July 27, 2012. The spill occurred on a leg of Enbridge's Lakehead Pipeline System, which transports oil from Neche, N.D., to Chicago, Ill., and to Buffalo, NY. The system includes 10 pipelines plus numerous pumping and maintenance facilities. Lakehead Pipeline System is the same system that failed July 25, 2010, leading to a massive 3.2 million-litre (20,000 barrel) oil spill into Michigan's Kalamazoo River. In response the U.S. Transportation Department's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) has ordered Enbridge to perform a comprehensive safety review of its entire 1,900-mile Lakehead oil delivery system before it can operate again. The order also requires Enbridge to hire an independent observer to evaluate the findings and certify the Lakehead Pipeline System is safe to operate. "We want to be sure the operator is addressing everything they can for the entire system so it operates safely," said PHMSA spokesman Damon Hill. A July 10, 2012 US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) report harshly criticized Enbridge for its initial response to the 2010 Michigan spill. The report prompted the National Energy Board in Canada to announce it will increase safety audits on the company's Canadian operations in the coming months. These reports and spills raise concerns about the safety of Enbridge's plan to build a pipeline to deliver crude bitumen from the Alberta oilsands to tankers on the B.C. coast. Environmental review hearings are underway and the federal government has set a Dec. 31, 2013 deadline for the panel's report on the Northern Gateway project. Canada's Conservative government is a strong supporter of the Northern Gateway Pipeline, but in the wake of Enbridge's spill in Wisconsin Canadian Heritage Minister James Moore has questioned Enbridge's safety record as: "not one that ... any other company should follow if they want to do business in British Columbia." "This project [Northern Gateway Pipeline] will not survive public scrutiny unless Enbridge takes far more seriously their obligation to engage the public and to answer those very legitimate questions about the way in which they've operated their business in the very recent past," added Moore. Moore's comments are significant because this is the first time any top Canadian government official has questioned the Enbridge Northern Gateway Pipeline. View August 3, 2012 Planet Ark coverageView August 3, 2012 Financial Post coverage View August 3, 2012 CTV coverage View August 2, 2012 The Globe and Mail article View August 2, 2012 Inside Climate News View August 1, 2012 U.S. Transportation Department's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration Order to Enbridge (PDF) View August 1, 2012 Wisconsin Superior Telegram coverage View July 29, 2012 Los Angeles Times coverage View July 13, 2012 Manitoba Wildlands news item Sources: Inside Climate News, Planet Ark, Financial Post, CTV
 The United States (US) National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) issued a scathing report July 10, 2012 finds that Alberta-based Enbridge had poorly maintained a section of pipeline that ultimately spilled 20,000 barrels (nearly 3.2 million litres) of diluted bitumen from Alberta's oilsands into the Kalamazoo River in Michigan July 25, 2010.
The United States (US) National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) issued a scathing report July 10, 2012 finds that Alberta-based Enbridge had poorly maintained a section of pipeline that ultimately spilled 20,000 barrels (nearly 3.2 million litres) of diluted bitumen from Alberta's oilsands into the Kalamazoo River in Michigan July 25, 2010."This investigation identified a complete breakdown of safety at Enbridge. Their employees performed like Keystone Kops and failed to recognize their pipeline had ruptured and continued to pump crude into the environment," said NTSB Chairman Deborah Hersman. The NTSB report found that not only was Enbridge's response to the spill slow, but the company knew at least five years before the massive leak that the pipeline was corroded and cracked. Enbridge currently proposes to build a $5.5-billion, 1,177-kilometre Northern Gateway pipeline from the oilsands in northern Alberta to the west coast of British Columbia (BC). Most BC residents, municipalities, and First Nations already staunchly oppose the project due to concerns about oil spills from the pipelines and from oil tanker on the treacherous BC coastline. The US NTSB report has only served to bolster already strong opposition to the Northern Gateway pipeline [in Canada.] "How can we trust Enbridge to build two pipelines safely across nearly 800 rivers and streams in Alberta and British Columbia?" ForestEthics spokesperson Nikki Skuce said in a statement. "I think the company should be deeply embarrassed about what unfolded. If they think they're going to operate like that in British Columbia – forget it," said BC Premier Christy Clark. Until now, Ms. Clark has not taken a public position on the Northern Gateway pipeline. The NTSB report has prompted the BC Premier to promise she will use BC's intervenor status in the current Northern Gateway Pipeline National Energy Board review to question Enbridge on its safety record. In Alberta the NTSB report, and a spat or recent pipeline spills, prompted more than 50 provincial organizations representing a broad cross-section of Alberta's population to issue an open letter calling on Alberta Premier Alison Redford to establish an independent inquiry into pipeline safety in Alberta. View July 25, 2012 United States (US) National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) reportView July 12, 2012 Alberta Surface Rights Group/Council of Canadians press release View July 11, 2012 Globe and Mail coverage View July 11, 2012 Metro News coverage View July 10, 2012 United States National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) press release View July 10, 2012 Pembina Institute blog post View July 10, 2012 Straight.com coverage View July 10, 2012 Globe and Mail coverage View July 10, 2012 CBC News coverage Sources: US NTSB, Globe and Mail, Alberta Surface Rights Group/Council of Canadians
 The Canadian joint review panel (JRP) hearings, on whether to approve the Enbridge Northern Gateway pipeline, which would deliver crude from Alberta's oilsands to Kitimat, British Columbia (B.C.), for shipment to Asia, began January 10, 2012. More than 4,300 people signed up to address the joint review panel regarding the proposed pipeline. The hearing process is expected to take 18 months.
The Canadian joint review panel (JRP) hearings, on whether to approve the Enbridge Northern Gateway pipeline, which would deliver crude from Alberta's oilsands to Kitimat, British Columbia (B.C.), for shipment to Asia, began January 10, 2012. More than 4,300 people signed up to address the joint review panel regarding the proposed pipeline. The hearing process is expected to take 18 months.One day before the JRP hearing were set to begin Canada's Natural Resources Minister Joe Oliver released an open letter which claimed foreign and radical groups "threaten to hijack our regulatory system to achieve their radical ideological agenda," stack the hearings with people to delay or kill "good projects," attract "jet-setting" celebrities and use funding from "foreign special interest groups." "Why has the Minister resorted to name calling? Apparently he's upset that 4,300 people have asked to participate in the Northern Gateway environmental assessment joining with 100 First Nations communities who strongly object to the scheme," said Sierra Club Canada Executive Director John Bennett. "Just because a lot of people want to talk, it doesn't mean the process is broken. In fact, a lot of people would say the opposite," said Gerald Butts, president and CEO of WWF Canada. "We question how the three National Energy Board panelists, who were appointed by the federal government, can fairly review this proposal when the Prime Minister and Minister of Environment openly promote what they perceive as the necessary outcome? In the end, it will be the federal government which decides on the panel's report, a decision that has apparently already been made," said Grand Chief Edward John, Hereditary Chief of Tl'azt'en Nation in northern B.C. "It is not First Nations, conservation groups or individual opponents that are radical. They seek to protect the fundamental nature of the wilderness of northern British Columbia, the ecological health of British Columbia coastal eco-systems, and the integrity of impartial environmental review. It is your government that is radical by proposing quite radical alteration of those values," said Elizabeth May. Dene National Chief Bill Erasmus said that Minister Oliver's open-letter "pits people against each other. The federal government should be brining people together. That should be the focus." View January 13, 2012 Indian Country Today articleView January 12, 2012 Aboriginal Peoples Television Network (APTN) article View January 9, 2012 Open-letter from Joe Oliver, Canada Minister of Natural Resources View January 9, 2012 Open-letter from Elizabeth May, Canadian Green Party Leader View January 9, 2012 Open-letter from John Bennett, Executive Director Sierra Club Canada View January 11, 2012 CTV News article View January 9, 2012 Canadian Press article Listen January 11, 2012 CBC Radio On The Coast coverage View January 9, 2012 CBC News article View January 6, 2012, January 9, 2012, January 9, 2012 Globe and Mail articles Source: Globe and Mail & APTN
Resources Canada Inc. (EOG) is proposing to construct the Waskada Pipeline Project (Public Registry file 5450.00). The proposed pipeline would be approximately 104 km long, 219.1 mm O.D. pipeline to transport oil from the Waskada Battery to the Tundra facility near Cromer, Manitoba. Construction is scheduled to begin as soon as regulatory approvals are in hand and the proponents plan to have the pipeline in service by the fourth quarter of 2010. The pipeline is intended to link new oil wells in the project area. Some land owners have refused access to their lands for surveying, and to date a plan to use an existing rail right of way for the pipeline has failed to meet local approval. Field work had not been conducted when the proposal was filed under the Act, and the consultants for the project plan indicated that public open house materials had very little text included. EOG Resources has submitted their Environmental Assessment (EA) Plan under Manitoba's Environment Act, for public review of the project. The EA outlines the proposed area for the pipeline, potential effects of construction to the area, potentially affected species, potential environmental and socio-economic effects, and potential cumulative effects. Manitoba Wildlands participated in this public review, and has submitted review comments for this project.  Download Manitoba Wildlands Comments: Environmental Assessment Review for Waskada Pipeline Project (PDF) Download Manitoba Wildlands Comments: Environmental Assessment Review for Waskada Pipeline Project (PDF)  Manitoba Hydro Overview Energy production and distribution in Manitoba is inextricably linked to its publicly owned utility. Manitoba Hydro serves 510 000 electric customers throughout Manitoba and 258 000 natural gas customers in various communities throughout southern Manitoba. Energy production and distribution in Manitoba is inextricably linked to its publicly owned utility. Manitoba Hydro serves 510 000 electric customers throughout Manitoba and 258 000 natural gas customers in various communities throughout southern Manitoba.Source: Manitoba Hydro
The utility has several roles:
Electricity Production
 Close to 98% of the electricity Manitoba Hydro generates is produced by the 14 hydroelectric generating stations on the Nelson, Winnipeg, Saskatchewan and Laurie Rivers. Approximately 2% of Manitoba Hydro's electricity is produced by two thermal generating stations and four remote diesel generating stations.
Close to 98% of the electricity Manitoba Hydro generates is produced by the 14 hydroelectric generating stations on the Nelson, Winnipeg, Saskatchewan and Laurie Rivers. Approximately 2% of Manitoba Hydro's electricity is produced by two thermal generating stations and four remote diesel generating stations.Source: Manitoba Hydro
In total, Manitoba Hydro's electric power generating capacity is 5,481MW, and of this 4,998MW comes from hydroelectric generating stations. Manitoba Hydro purchases electricity generated by wind turbines - as of February 2007, Manitoba is generating 103.95MW of electricity from Phase 1 and Phase 2 of the St. Leon project. Source: Canadian Wind Energy Association
Wind power therefore supplies just under 2% of Manitoba's total electricity generation capacity. In 2005, and again in 2006 the Manitoba Government committed to development of 1,000MW of wind power over the next decade. Source: Government of Manitoba
Other proposed wind projects are being reviewed under the Environment Act (see New Renewable Energy - Wind Energy below). Agreements must also be in place between independent power producers and Manitoba Hydro to integrate this power into Manitoba Hydro's transmission system. To date there are no public environmental statement standards for wind developers to fulfill for their Manitoba environmental license. Manitoba Hydro has extensive infrastructure to support delivery of power in the province. There is roughly 11,000km of transmission corridors throughout the province, outside towns and cities. The transmission system transports electricity at high voltages from the generating stations to other parts of Manitoba Hydro's provincial power system, as well as to other utilities' power systems. The distribution system transforms the higher voltages to useable levels for delivery to customers, and maintains steady voltage levels in spite of continuously changing demands for power during the course of a day or a season.
Source: Manitoba Hydro
There are 12 points or interconnections between Manitoba Hydro's transmission infrastructure and the electricity grids of other Canadian provinces and the US. They provide the capacity for Manitoba to import approximately 850MW and export 2,600MW of power. Manitoba Hydro claims ability to export surplus power is a major factor in keeping Manitobans' electricity costs at low rates. Natural Gas Purchasing and Distribution
Manitoba Hydro-owned Centra Gas purchases natural gas from suppliers and delivers the gas to Manitoba consumers. In order to move the gas to where it is needed, Centra maintains 1674 km of transmission pipeline and 6496 km of distribution pipeline.Source: Manitoba Hydro
Support for Energy Conservation
 Manitoba Hydro has an energy conservation strategy (also known as 'demand-side management') called 'Power Smart' (please also see section below on New Renewable Energy - Energy Conservation). The objective of Power Smart is to meet energy needs through efficiency improvements rather than new sources of generation. Through Power Smart, Manitoba Hydro promotes energy efficient products, services and programs for residential, commercial and industrial customers.
Manitoba Hydro has an energy conservation strategy (also known as 'demand-side management') called 'Power Smart' (please also see section below on New Renewable Energy - Energy Conservation). The objective of Power Smart is to meet energy needs through efficiency improvements rather than new sources of generation. Through Power Smart, Manitoba Hydro promotes energy efficient products, services and programs for residential, commercial and industrial customers.Source: Manitoba Hydro
Manitoba Hydro's Earth Power Loan Program provides assistance to Manitobans wishing to install geothermal heat pumps. Geothermal heat pumps, often referred to as GeoExchange or Earth Energy, use a system of pipes buried below the frost line, where the ground is warmer in winter and cooler in summer to provide heating and cooling for homes and businesses. They emit 66% less greenhouse gases than conventional heating and cooling systems that use fossil fuels and use up to 75% less electricity, reducing annual heating and cooling costs by 50% - 70%. Installations have tripled over four years and Manitoba has become a leader in earth energy systems, including for manufacturing of systems.  Manitoba programs to promote residential or commercial installations of solar energy, for heating water are new. Manitoba does noes not have an electricity feed law that would permit individuals to connect their solar power systems to the grid and pay them a fair price to 'feed' electricity back into the grid when not being used by the household.
Manitoba programs to promote residential or commercial installations of solar energy, for heating water are new. Manitoba does noes not have an electricity feed law that would permit individuals to connect their solar power systems to the grid and pay them a fair price to 'feed' electricity back into the grid when not being used by the household.
Manitoba Energy PlanDuring the absence of these public policy tools, various Manitoba Hydro development intentions/proposals continue to be actively discussed, planned, and/or proposed. These projects, if approved, have the potential to alter significant tracts of our northern boreal forest ecosystems. They are being planned without completed networks of protected areas in these forest regions. The government's development intentions are geared towards serving out-of-province/ export energy markets. Manitoba currently has sufficient energy for domestic purposes. In 2002, a new provincial Department of Energy, Science and Technology (EST) was created. Visit Manitoba Department of Energy, Science and Technology website Visit Manitoba Hydro website View Manitoba government press releases about Manitoba Hydro Manitoba's need for an energy plan was recognized by the Manitoba Chambers of Commerce (MCC), which called, in 2006, for a public dialogue to arrive at an energy plan for Manitoba. The MCC passed a resolution - An Energy Plan for Manitoba at its 75th Annual General Meeting (AGM) March 2006. One of the primary objectives of the MCC resolution would be to "define environmental protection and conservation of our natural ecosystems as primary considerations in terms of energy use in Manitoba." As Manitoba's largest business lobby, the MCC represents 74 communities and over 10,000 businesses across Manitoba through direct corporate membership and local chambers.  Download March 2006 Manitoba Chambers of Commerce resolution An Energy Plan for Manitoba (PDF) Download March 2006 Manitoba Chambers of Commerce resolution An Energy Plan for Manitoba (PDF)Visit the Manitoba Chambers of Commerce web site New Renewable EnergyVisit Manitoba Government's Energy Development Initiative web site The Manitoba Government has taken some initial steps to promote the development of alternative and new renewable sources of energy. In this section we are providing information on government programs and initiatives related to this commitment to energy alternatives as well as energy projects that have been proposed or are in the process of being licensed. Energy Conservation
Conservation is an often overlooked but very important source of alternative energy. The Manitoba Hydro Power Smart Program, has not realized the full potential of demand side management (DSM) opportunities.
Visit Manitoba Hydro's PowerSmart pages Visit the following sites for energy efficiency and DSM best practices: Best Practices Benchmarking for Energy Efficiency Programs Canadian Energy Efficiency Centre Manitoba Wildlands reviewed the Manitoba Energy Science and Technology Hydrogen Discussion paper.  Download An Evaluation of Preliminary Hydrogen Opportunities Report Download An Evaluation of Preliminary Hydrogen Opportunities Report  (PDF) (PDF)View the Preliminary Hydrogen Opportunities Report View Pembina Institute Fact Sheet: Wind Power Realities As of January 2009, twelve wind energy projects have been proposed or licensed under Manitoba's Environment Act. It is not clear in licensing policy for Manitoba wind projects how the changing output of energy from wind turbines (up to the MW a project is licensed for) affects ability to add to a project.
 The St. Leon Wind Energy Project is a 99 MW wind project located approximately 150 kilometers southwest of Winnipeg near the town of St. Leon and Swan Lake First Nation in Manitoba. It is the only wind project operating in Manitoba. The St. Leon Wind Energy Project is a 99 MW wind project located approximately 150 kilometers southwest of Winnipeg near the town of St. Leon and Swan Lake First Nation in Manitoba. It is the only wind project operating in Manitoba.The project was licensed in November 2003 under Manitoba's Environment Act as a Class 2 Development (for more information on Class 1, 2 and 3 licences, go here) to Sequoia Energy. The project has since been acquired by Algonquin Power and became the St. Leon Wind Energy Limited Partnership. View Algonquin Power information about St. Leon Wind Energy ProjectThe initial Manitoba government environmental licence for the St. Leon Wind Energy Project (PR File # 4976.00) has been revised four times since 2003, with the most recent licence issued in December 2007 (Licence: 2629 RRRR (PDF)). Construction of the wind project occurred over a number of years, with the project being declared a 'commercial operation' by Algonquin Power in September 2007. 'Commercial operation' can have a variety of meanings, depending on the agreement. September 2007, the project met Algonquin Power's definition of 'commercial operation', as "substantially complete". Commercial Operation, based on the power purchase agreement with Manitoba Hydro, began in 2006; when St. Leon began generating electricity. View October 31, 2007 Algonquin Power,St. Leon Wind Project announcementThe St. Leon Wind Project consists of sixty-three 1.65 MW Vestas V82 Wind Turbine-Generators. The turbines stand 80 metres tall, with a rotor diameter of 82 metres. Each turbine assembly weighs approximately 220 tonnes. Turbines start generating at a minimum wind speed of three metres per second, always turning at 14.4 rpm. This development also includes access roads, a collector substation, and an operations and maintenance building. A 99 MW wind project is capable of powering approximately 41,000 homes.  The St. Joseph Wind Energy Project is one of 84 proposals filed with Manitoba Hydro in response to its 2007 request for proposals (RFP) for 300MW of wind power. (This RFP process is based on the Manitoba government's commitment to 1000 MW of wind energy.) The St. Joseph Wind Energy Project is one of 84 proposals filed with Manitoba Hydro in response to its 2007 request for proposals (RFP) for 300MW of wind power. (This RFP process is based on the Manitoba government's commitment to 1000 MW of wind energy.)In November 2007, the Manitoba government announced the St. Joseph project had been selected and Manitoba Hydro would begin to negotiate a power purchase agreement. View November 2004, 2007 Government of Manitoba press releaseIn July 2008, BowArk Energy and Babcock & Brown's North American Energy Group filed a proposal under the Manitoba Environment Act for St. Joseph Wind Energy Project (PR File #5353.00). View information about St. Joseph Wind Energy Project from BowArk EnergyThe St. Joseph Wind Energy Project is to be located in the rural municipalities of Montcalm and Rhineland south of Winnipeg, east of the Red River, and close to the US border. More than 250 landowners are involved in or affected by the project that spans 44,000 acres of land. Forty km of new access roads will be required. An addendum to the St. Joseph Environment Act Proposal was filed June 2009. The primary change is the switch from GE 1.5 MW turbines to Siemens 2.3 MW turbines, reducing the number of turbines from 200 to 130. The new turbines have a slightly larger router diameter and are substantially quieter. View Manitoba Government online registry for St. Joseph Wind Energy ProjectView July 11, 2009 Steinbach Online.com article The parent company, Babcock and Brown Infrastructure North America has, as of August 24th 2009, been forced to sell off its North American assets. As a result, Riverstone Holdings LLC has purchased the wind development portfolio from Babcock and Brown to form Pattern Energy Group LP, an independent, fully integrated energy company that develops, constructs, owns and operates renewable energy, now including St. Joseph Wind Farm Inc. The Wind farm project is still planned to go ahead as there has been no indication otherwise, but there are no new developments as to when construction will begin or if it will be on the same scale as was originally expected.
After a year long delay due to financial problems with the parent company Babcock and Brown, the Pattern Energy owned St. Joseph's wind project is going to produce only 138 megawatts of energy compared to the 300 megawatts originally planned. St. Joseph's wind project was going to be the largest wind project in Canada and decrease in size will affect revenue for municipalities and landowners involved. The decrease in generation also effects Manitoba's goal of reaching 1000 MW of wind energy by 2015, since nine other licensed wind projects have been put on hold. Pattern Energy is apparently looking to the Manitoba Government to subsidize the project, an act not all officials agree with. Manitoba Hydro says the power purchase agreement is almost complete. View Manitoba Legislative Assembly Transcripts for Nov 17, 2009 (PDF)View November 14, 2009 Winnipeg Free Press article View November 18, 2009 Winnipeg Free Press article View November 19, 2009 Steinbach Online.com press release Source: Winnipeg Free Press, Steinbach Online, Manitoba Legislative Assembly
St. Joseph's wind project have been in the works since 2008 but were on hold due to parent financing company Babcock and Brown financial difficulties. Pattern Energy of San Francisco bought Babcock and Browns projects including the St. Josephs project. The project had been downscaled from its original 300 megawatts to 138 mw, including a change in type of wind turbine. Pattern Energy will invest $95 million and Manitoba Hydro will loan 260 million to the company. Construction is to be finished by spring 2011 with 60 turbines up and running. View Public Registry for St. Joseph Wind Energy ProjectView March 4, 2010 Red River Valley Echo news article View March 21, 2010 CBC News article View March 22, 2010 Manitoba Government press release View March 24, 2010 Project Finance article Sources: CBC News, Manitoba Government
 Turbines at St. Joseph Wind Energy project began producing electricity January 11, 2011. When fully operational the project will produce enough electricity for 50,000 homes.
Turbines at St. Joseph Wind Energy project began producing electricity January 11, 2011. When fully operational the project will produce enough electricity for 50,000 homes.The project, initially slated to have a electrical generation capacity of 300 megawatts (MW) was scaled down to 138MW and largely financed by Manitoba Hydro after private financial backers pulled out. Three separate Government of Manitoba Orders in Council (#88-90) issued March 18, 2010 authorized the financing and operation of the St. Joseph wind energy project located near Letellier, Manitoba. Under the arrangement the $345 million dollar project was funded with $95 million from Pattern Energy and a $250-260 million Manitoba Hydro loan to the St. Jospeh Wind Farm Inc. Repayments to the loan are to be deducted against what Manitoba Hydro owes for power purchased, and in the case of default hydro takes ownership of the wind towers. Six years ago, the province set a target of producing 1,000 megawatts of power from wind within a decade, but it's likely to fall short of that. View January 11, 2011 Manitoba Government news releaseView January 11, 2011 CTV News article View January 12, 2011 Winnipeg Free Press article View January 15, 2011 Winnipeg Free Press article  Download Manitoba Order in Council (00088 /2010) (PDF) Download Manitoba Order in Council (00088 /2010) (PDF) Download Manitoba Order in Council (00089 /2010) (PDF) Download Manitoba Order in Council (00089 /2010) (PDF) Download Manitoba Order in Council (00090 /2010) (PDF) Download Manitoba Order in Council (00090 /2010) (PDF)View Manitoba Hydro 59th Annual Report (pg. 28 online – 26 print) View March 29, 2010 Manitoba Wildlands news item Sources: Manitoba Government, Manitoba Hydro, Winnipeg Free Press  Concerns have been raised because ten of the eleven projects licensed or in the process of obtaining an environmental licence in Manitoba are 99 MW projects. This avoids classification as a Class 3 development (projects under 100 MW are Class 2 developments) under the Environment Act, resulting in lower licensing fees, less public involvement, no public hearings, and no EIS Guidelines.
Concerns have been raised because ten of the eleven projects licensed or in the process of obtaining an environmental licence in Manitoba are 99 MW projects. This avoids classification as a Class 3 development (projects under 100 MW are Class 2 developments) under the Environment Act, resulting in lower licensing fees, less public involvement, no public hearings, and no EIS Guidelines.View Manitoba wind projects environment licence chart Currently, despite political commitments to avoid staged environmental licenses in Manitoba, these 99 MW project developers assume they can add to their projects without having to be assessed, etc. Also there are no public EIS standards in Manitoba for wind energy projects. An example of what this means is that there are no set back standards. Manitoba Wildlands provided comments on some wind energy projects that have or are been assessed under Manitoba's Environment Act. Download Manitoba Wildlands/CNF October 17, 2003 comments: Sequoia Energy Inc. - St. Leon Wind-Energy Project Download Manitoba Wildlands/CNF October 17, 2003 comments: Sequoia Energy Inc. - St. Leon Wind-Energy Project  (PDF) (PDF) Download Manitoba Wildlands/CNF December 12, 2003 appeal of the November 14, 2003 environmental license for Sequoia Energy Inc. - St. Leon Wind-Energy Project Download Manitoba Wildlands/CNF December 12, 2003 appeal of the November 14, 2003 environmental license for Sequoia Energy Inc. - St. Leon Wind-Energy Project  (PDF) (PDF) Download Manitoba Wildlands' March 8, 2006 comments: Killarney Wind Energy Project Download Manitoba Wildlands' March 8, 2006 comments: Killarney Wind Energy Project  (PDF) (PDF) Download Manitoba Wildlands' April 12, 2006 comments: Dacotah Wind Energy Project Download Manitoba Wildlands' April 12, 2006 comments: Dacotah Wind Energy Project  (PDF) (PDF)Other individuals and groups, including landowners/farmers in Manitoba, also raised concerns and provided comments on wind energy projects that have are being licensed under Manitoba's Environment Act. Some of the concerns raised by farmers and landowners about effects from the 99 MW Swan Lake Wind Energy Project (Greenwing Energy Development L.P.) include:
View the November 21, 2005 Government of Manitoba press release  The invitation for expressions of interest in wind power projects resulted in 36 responses from 43 proponents including wind developers, First Nations, communities, turbine manufacturers and consultants.
The invitation for expressions of interest in wind power projects resulted in 36 responses from 43 proponents including wind developers, First Nations, communities, turbine manufacturers and consultants.View the March 10, 2006 Government of Manitoba press release In September 2006, the Manitoba Government took the next step towards its goal of 1,000 MW of wind power, announcing another request for proposals for 300 MW of private land to take place in winter 2006-07. View September 7, 2006 Government of Manitoba press release View Manitoba Crown land and federal wind project polices in the links below.  Download September 14, 2006 Manitoba Crown Land Policy and Wind Farms (PDF) Download September 14, 2006 Manitoba Crown Land Policy and Wind Farms (PDF) Download 2003 Canadian Wind Power Production Incentive EIS Guidelines (PDF) Download 2003 Canadian Wind Power Production Incentive EIS Guidelines (PDF)The Canadian Wind Energy Association (CanWEA) website maintains up to date information regarding installed wind project and wind projects that have been contracted or are under construction.  Download Canadian Wind Energy Association June 2009 chart of wind power Initiatives across Canada Download Canadian Wind Energy Association June 2009 chart of wind power Initiatives across CanadaView a chart of installed wind capacity by province  Download Canada's current installed wind capacity (PDF) Download Canada's current installed wind capacity (PDF)Manitoba Hydro – Development IntentionsSee our Consultations/Licenses page, and links regarding environmental licenses above for information about the Manitoba Hydro license application for Wuskwatim generation station and transmission line projects. See Manitoba Hydro for maps of the hydroelectric system in Manitoba and information regarding the corporation's development intentions. |
||||||||||
Current major development intentions include:
|
Manitoba Hydro - Current & Potential Interconnections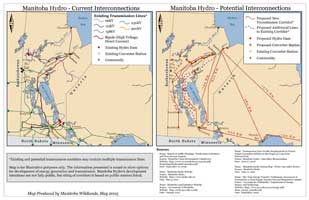 Larger Image |
| Manitoba Wildlands has mapped both existing and potential transmission lines/corridors for Manitoba. See the inset map (right) regarding unknown transmission lines for new dams on the Nelson River. Citations and sources are listed on the main map (above right). | Potential Hydro Transmission - East Side of Lake Winnipeg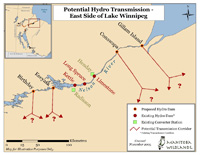 Larger Image |
Wuskwatim Projects
Manitoba Hydro Projects
Historic Hydro Gallery Manitoba Wildlands hydro photo gallery shows communities and rivers across northern Manitoba, starting as early as 1880, to show before, during, and after images of hydro generation development in our province. Manitoba Wildlands hydro photo gallery shows communities and rivers across northern Manitoba, starting as early as 1880, to show before, during, and after images of hydro generation development in our province.For information click here |
Hydro Research
Hydro Map Gallery
Comment |
 |
Manitoba Hydro: 10 things Manitobans need to know Manitoba Hydro's development plans are a constant feature of media coverage, in particular because of a growing preoccupation with climate change and messaging that portrays hydroelectric power as climate-friendly. Some content implies that new dams in Manitoba will deliver on Kyoto obligations by exporting energy. Manitoba Hydro is actively planning new hydroelectric dams and transmission lines. The licensing process for the first of a 'new generation' of hydro projects - the Wuskwatim Generating Station and Transmission projects began in November 2001. Federal approvals and provincial environment licences were issued summer 2006. Manitoba Hydro's development plans are a constant feature of media coverage, in particular because of a growing preoccupation with climate change and messaging that portrays hydroelectric power as climate-friendly. Some content implies that new dams in Manitoba will deliver on Kyoto obligations by exporting energy. Manitoba Hydro is actively planning new hydroelectric dams and transmission lines. The licensing process for the first of a 'new generation' of hydro projects - the Wuskwatim Generating Station and Transmission projects began in November 2001. Federal approvals and provincial environment licences were issued summer 2006.Manitoba Hydro is a public utility owned by all Manitoba residents. The utility also owns natural gas distribution for the province. Every Manitoban is affected by Manitoba Hydro's investment decisions and debt load. 10 facts each Manitoban should know:
| |
 2002-2014
2002-2014


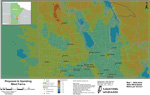
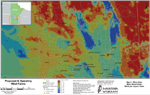
 At a November 2009 Manitoba Legislature crown corporations committee hearing Manitoba Hydro announced the proposed St. Joseph's wind project will be less than half its original size.
At a November 2009 Manitoba Legislature crown corporations committee hearing Manitoba Hydro announced the proposed St. Joseph's wind project will be less than half its original size. Premier Greg Selinger announced in March 2010 the St. Joseph's wind project in southern Manitoba, west of highway 75, and just north of the US Canada border, will go ahead. The 138-megawatt wind project got the go ahead with a 27- year power purchase deal between Manitoba Hydro and Pattern Energy Group.
Premier Greg Selinger announced in March 2010 the St. Joseph's wind project in southern Manitoba, west of highway 75, and just north of the US Canada border, will go ahead. The 138-megawatt wind project got the go ahead with a 27- year power purchase deal between Manitoba Hydro and Pattern Energy Group.